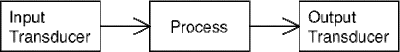electricals
Popular Posts
-
A transducer is a device which converts a signal from one form to another. Most electronics circuits use both input and output transdu...
-
*A Scott-T transformer (also called a Scott connection) is a type of circuit used to derive two-phase (2-φ) current from a three-phase (3-...
-
Mesh Analysis : This is also called Loop Analysis.This method uses simultaneous equations, Kirchhoff's Voltage Law, and Ohm's Law t...
-
A clock generator is a circuit that produces a timing signal (known as a clock signal and behaves as such) for use in synchronizing a circui...
-
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity , electronics and ele...
-
Electrical Engineering Rankings 2011 Rank Title Country Academic Employer Citations Score 1 Massachusetts Institute of Technology (...
-
1. What types of CMOS memories have you designed? What were their size? Speed? Configuration Process technology? 2. What work have you d...
-
In an autotransformer portions of the same winding act as both the primary and secondary. The winding has at least three taps where electric...
Friday, 27 November 2015
Electrical Power Distribution System
Thursday, 24 April 2014
ONE-LINE DIAGRAM
Tuesday, 25 June 2013
Wednesday, 29 August 2012
TRANSDUCERS
Tuesday, 6 March 2012
SCOTT CONNECTION
*A Scott-T transformer (also called a Scott connection) is a type of circuit used to derive two-phase (2-φ) current from a three-phase (3-φ) source or vice-versa. The Scott connection evenly distributes a balanced load between the phases of the source.
*The Scott-T transformer connection may be also be used in a back to back T to T arrangement for a three-phase to 3 phase connection. This is a cost saving in the smaller kVA transformers due to the 2 coil T connected to a secondary 2 coil T in-lieu of the traditional three-coil primary to three-coil secondary transformer. In this arrangement the X0 Neutral tap is part way up on the secondary teaser transformer (see below). The voltage stability of this T to T arrangement as compared to the traditional 3 coil primary to three-coil secondary transformer is questioned.
*Nikola Tesla's original polyphase power system was based on simple to build two-phase components. However, as transmission distances increased, the more transmission line efficient three-phase system became more prominent. Both 2-φ and 3-φ components coexisted for a number of years and the Scott-T transformer connection allowed them to be interconnected.
*Assuming the desired voltage is the same on the two and three phase sides, the Scott-T transformer connection (shown below) consists of a center-tapped 1:1 ratio main transformer, T1, and an 86.6% (0.5√3) ratio teaser transformer, T2. The center-tapped side of T1 is connected between two of the phases on the three-phase side. Its center tap then connects to one end of the lower turn count side of T2, the other end connects to the remaining phase. The other side of the transformers then connect directly to the two pairs of a two-phase four-wire system.
Friday, 13 January 2012
Clock generator
A clock generator is a circuit that produces a timing signal (known as a clock signal and behaves as such) for use in synchronizing a circuit's operation. The signal can range from a simple symmetrical square wave to more complex arrangements. The basic parts that all clock generators share are a resonant circuit and an amplifier.
The resonant circuit is usually a quartz piezo-electric oscillator, although simpler tank circuits and even RC circuits may be used.
The amplifier circuit usually inverts the signal from the oscillator and feeds a portion back into the oscillator to maintain oscillation.
The generator may have additional sections to modify the basic signal. The 8088 for example, used a 2/3 duty cycle clock, which required the clock generator to incorporate logic to convert the 50/50 duty cycle which is typical of raw oscillators.
Other such optional sections include frequency divider or clock multiplier sections. Programmable clock generators allow the number used in the divider or multiplier to be changed, allowing any of a wide variety of output frequencies to be selected without modifying the hardware.
The clock generator in a motherboard is often changed by computer enthusiasts to control the speed of their CPU, FSB, GPU and RAM. Typically the programmable clock generator is set by the BIOS at boot time to the value selected by the enthusiast; although some systems have dynamic frequency scaling that frequently re-program the clock generator.
The resonant circuit is usually a quartz piezo-electric oscillator, although simpler tank circuits and even RC circuits may be used.
The amplifier circuit usually inverts the signal from the oscillator and feeds a portion back into the oscillator to maintain oscillation.
The generator may have additional sections to modify the basic signal. The 8088 for example, used a 2/3 duty cycle clock, which required the clock generator to incorporate logic to convert the 50/50 duty cycle which is typical of raw oscillators.
Other such optional sections include frequency divider or clock multiplier sections. Programmable clock generators allow the number used in the divider or multiplier to be changed, allowing any of a wide variety of output frequencies to be selected without modifying the hardware.
The clock generator in a motherboard is often changed by computer enthusiasts to control the speed of their CPU, FSB, GPU and RAM. Typically the programmable clock generator is set by the BIOS at boot time to the value selected by the enthusiast; although some systems have dynamic frequency scaling that frequently re-program the clock generator.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)